GLP-1 + Gastrin: Next gen regenerative therapy
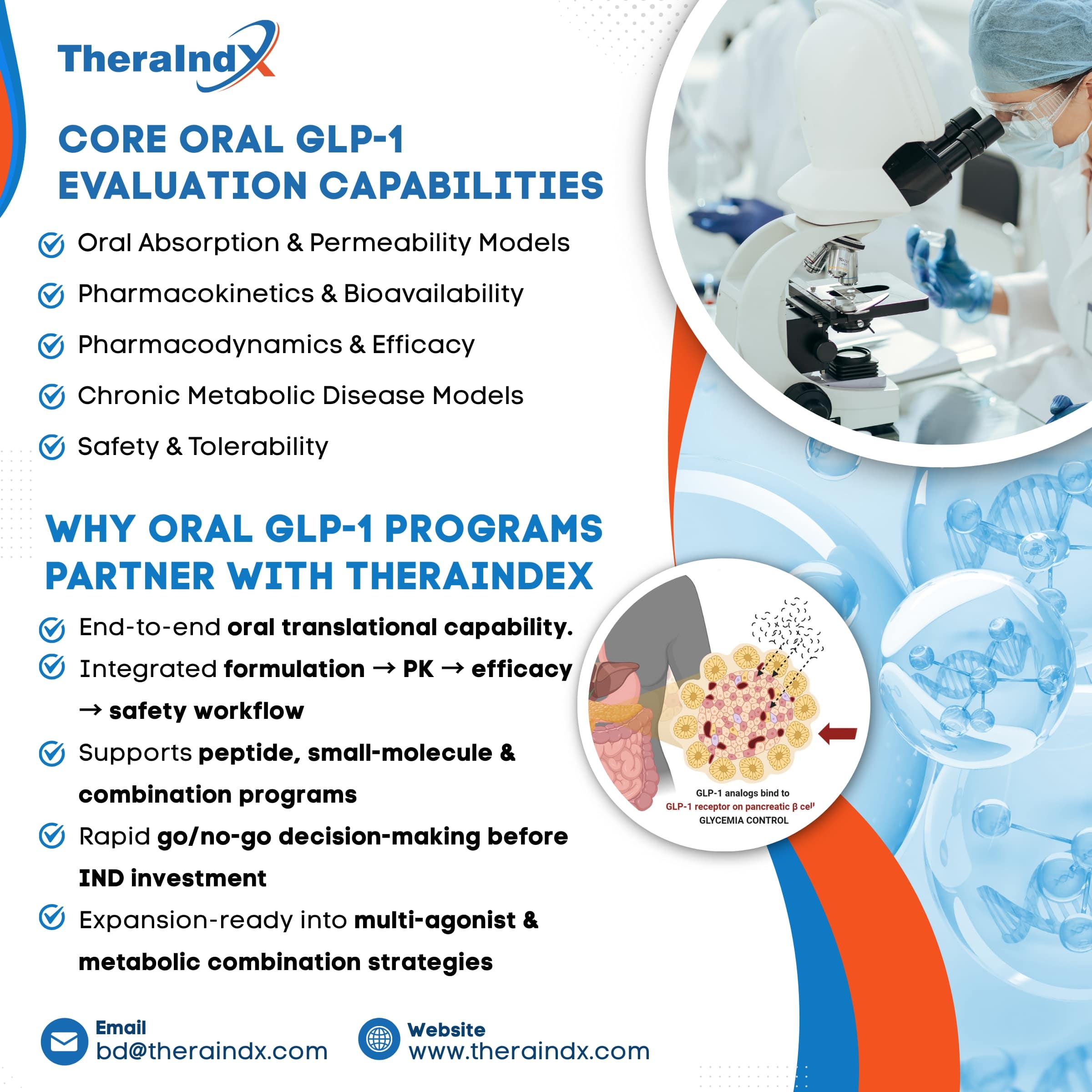
Diabetes mellitus continues to cause a global health challenge with over 500 million people affected worldwide. Incretin based therapies such as GLP-1 receptor agonists have revolutionised management of type 2 diabetes by enhancing insulin secretion, slowing gastric emptying and reducing appetite (Dungan & DeSantis, 2025).
GLP-1 + Gastrin is emerging as one of the most compelling innovations in the regenerative endocrinology. Supported by translational research, this approach aims not only to improve glucose control but also enhance β-cell survival and rebuild functional pancreatic islet mass (Natalicchio & Perrini, 2021; Duttaroy et al., 2017).
Why GLP-1 + Gastrin?
- - Increased β-cell proliferation
- - Enhanced β cell survival with reduced apoptosis
- - Restoration of islet mass in preclinical metabolic models
- - Improved glucose stimulated insulin secretion
This synergy has ensured success in regenerative therapies for type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Role of TheraIndx
TheraIndx is at the forefront of regenerative incretin therapy by offering:
- - Advanced diabetes and obesity models: Type 1 diabetes (T1D), type diabetes (T2D), diet induced obesity model and genetic models such as ob/ob and NOD mice.
- - High-definition endpoints: β-cell mass quantification, 3D islet morphology and hormonal biomarker panels. These endpoints provide in depth mechanistic details.
- - Mechanistic insights: GLP-1, CCK-B and GIP pathways are integrated to assess β cell survival and progenitor activation.
- - Integrated pK/pD and safety: pharmacokinetics (pK), pharmacodynamics (pD) studies in addition to toxicology studies to ensure translational readiness for IND filing.
Why is GLP-1 + Gastrin gaining commercial momentum?
- - Next gen foundation: GLP-1 drugs have already shown clinical success with huge revenue generation annually. Gastrin combination offers another differentiation with high market potential.
- - Pipeline shift: Pharma companies are moving away from traditional therapies and investing more into multi-agonist therapies such as GLP-1/ glucagon, GLP-1/Gastrin to achieve high efficacy with minimum toxicity.
- - Disease modifying potential: GLP-1+ Gastrin could regenerate β cells helping researchers exploring long term solutions
- - Market Trend: Investors and biotech firms are investing more into therapies that go beyond symptom control and have the ability to offer long term benefits.
Critical evaluation
Strengths
- - Addresses unmet need for disease modifying diabetes therapies, also applicable to related metabolic diseases
- - Combines regenerative potential with metabolic control
- - Supported by robust preclinical models and biomarker endpoints
Limitations
- - Translational challenges in moving from preclinical models to human β cells regeneration
- - Long term safety must be carefully evaluated, given its role in gastric physiology
- - Regulatory guidelines for such therapies are still evolving.
- 1. Dungan, K., & DeSantis, A. (2025). Glucagon like peptide 1 based therapies for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. UpToDate.
- 2. Duttaroy, A., et al. (2017). Synergistic effects of GLP-1 and gastrin co-therapy on β-cell regeneration in models of diabetes. Endocrinology, 158(6), 2022–2035.
- 3. Natalicchio, A., & Perrini, S. (2021). Regenerative approaches for diabetes treatment: The role of incretins and polyhormonal therapies. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 12, 667870.